知识图谱实践项目二
第二代的知识图谱项目作出了如下升级:
- 新添
游戏作者 游戏类型主体 - 改变了爬虫的逻辑,使其可以爬取更多信息(效率有损失)
- 优化了知识图谱的关系
爬虫代码如下:
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# |
知识图谱代码如下:
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# |
基于 Django 的 Web 界面
Django 是一个由 Python 编写的开放源代码的 Web 应用框架
本篇博客先介绍一下 Django 的使用,然后展示一下我自己写的测试网页
建立 Django 项目
创建一个 HelloWorld 项目,使用命令行输入:
1 | django-admin startproject HelloWorld |
- HelloWorld: 项目的容器
- manage.py: 一个实用的命令行工具,可让你以各种方式与该 Django 项目进行交互
- HelloWorld/init.py: 一个空文件,告诉 Python 该目录是一个 Python 包
- HelloWorld/asgi.py: 一个 ASGI 兼容的 Web 服务器的入口,以便运行你的项目
- HelloWorld/settings.py: 该 Django 项目的设置/配置
- HelloWorld/urls.py: 该 Django 项目的 URL 声明; 一份由 Django 驱动的网站”目录”
- HelloWorld/wsgi.py: 一个 WSGI 兼容的 Web 服务器的入口,以便运行你的项目
使用如下命令启动:
1 | python manage.py runserver |
在浏览器中使用如下网址:
在 Django 里面加载 HTML 的 CSS 样式
对于 Django 而言,加载 HTML,Django 会通过 templates 文件夹中放置的 HTML 来加载,有时需要嵌入 CSS 和 JS 等样式
在根目录下创建一个 base_views.py 文件:
1 | from django.shortcuts import render |
修改该根目录下 urls.py 文件中的代码:
1 | from django.contrib import admin |
修改根目录下的 settings.py 中的代码:
1 | 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'HelloWorld/templates')], |
- 修改 TEMPLATES 下的 DIRS
此时 Django 默认是对 CSS、JS 的静态文件是拒绝访问的,必须要在里面进行配置才行:
- 在你建好的 Django 的根目录下新建 static 文件夹,在下面再新建 CSS,Images
- 在
settings.py文件进行相关配置,在STATIC_URL = '/static/'后面加入如下代码:
1 | STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'), ) |
最后需要对 html 进行修改,直接把 herf 链接写死
- 修改前:
1 | <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/normalize.css"> |
- 修改后:
1 | <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/normalize.css"> |
最后对从网上下载的 HTML 进行魔改:
效果如下:


- 关于 HTML 的编写不是本篇博客的重点,就略过了
基于 Echarts 的 Neo4j 可视化
在 Django 项目中使用 Neo4j
Django 可以把 Neo4j 中的知识图谱显示在前端页面上
我的做法是直接定义一个类用于连接 Neo4j:
1 | class Neo4j(): |
并在根目录下 urls.py 文件所添加的函数中使用 Neo4j 类
- 这里使用正则表达式来匹配 URL,如果匹配成功则调用后面的函数
1 | urlpatterns = [ |
这种做法其实就是把 Neo4j 当成了 Django 项目中的一个子模块
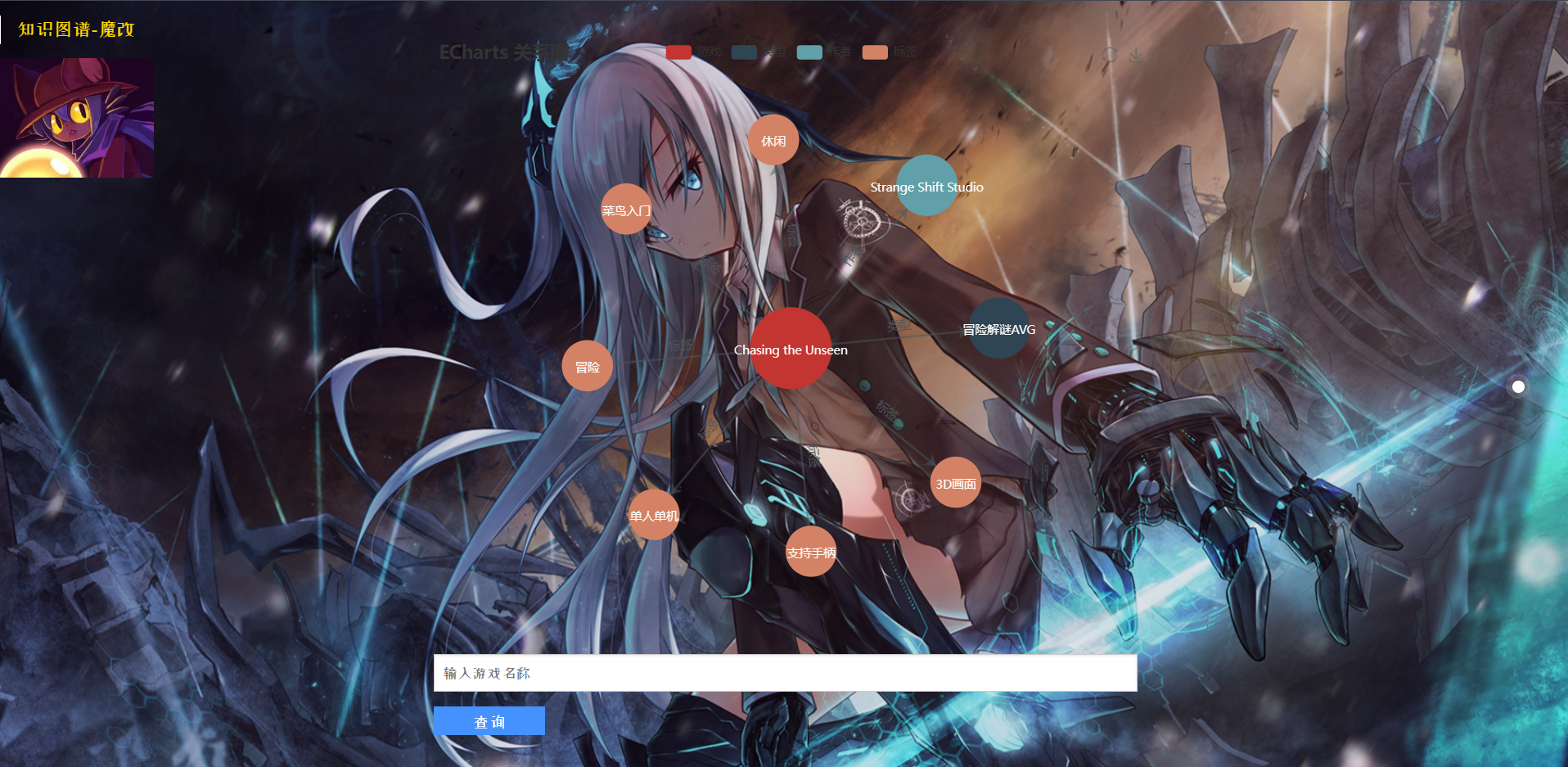
Echarts 实现知识图谱可视化
Echarts 是用 JavaScript 实现的开源可视化库
学习这个东西可花了我不少的力气,效果如下:
我实现的思路就是直接在 urls.py 中添加用于实现功能的函数:
1 | urlpatterns = [ |
1 | def searchDetail(request): |
- 识别 URL 中的
user_text并调用对应的函数(简单转换为 Cypher 语句) - 在 Neo4j 中查找数据,将返回的数据提交给 JavaScript 层
1 | def name2game(self,value): |
- 在 JavaScript 层中识别 Django 层函数返回的数据,简单处理后交给 Echarts:
1 | {% if ctx %} |
- 从
var myChart = echarts.init到myChart.setOption(option)都是 Echarts 的模板 - 如果对 Django 层返回的数据不熟悉,可以直接用
console.log(entityRelation)把该数据输出到控制台,并打开 F12 进行查看